The treatments used at OFN
Collectively the treatments we use are called "neuromodulation". We surgically implant electrodes into precise positions in the body, either in or next to parts of the nervous system. Most commonly, electrodes are placed in the brain or into the space next to the spinal cord. The electrodes are connected by wires running under the skin to a small device that contains a battery and sends small electrical pulses to the electrodes. The electrical pulses change (or "modulate") the way that part of the nervous system is working. This might be done for example in order to stop a tremor, or to block pain signals.
Deep brain stimulation
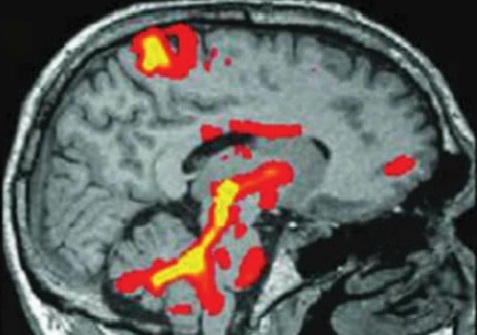
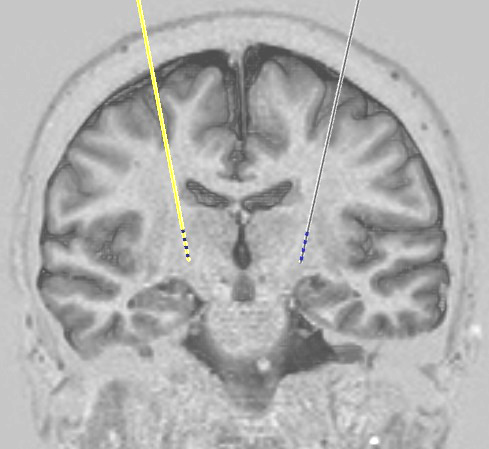
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves the implantation of electrodes in the brain. DBS is used to treat movement disorders including Parkinson's disease, dystonia, and certain types of tremor. It is also used in some circumstances to treat chronic severe pain.
Find out more about deep brain stimulation.
Spinal cord stimulation
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is used to treat chronic severe pain. Electrodes are implanted in the spine next to the spinal cord. We have used SCS to treat pain in the legs, back, abdomen and arms.
Find out more about spinal cord stimulation.
Dorsal root ganglion stimulation
In dorsal root ganglion stimulation (DRGS) an electrode is placed on a specific part of a nerve that is carrying sensory signals (including pain signals) from part of the body to the spinal cord, which then sends them to the brain. The electrode is placed on a bulge in the nerve just as it reaches the spine. Because we are simulating one nerve rather than the whole spinal cord, this works well when the pain is focussed in a particular area, for example the foot.
Find out more about dorsal root ganglion stimulation.
Occipital nerve stimulation
Occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) is used to treat migraine or cluster headache. Electrodes are placed underneath the scalp on the back of the head (an area known as the occiput).
Find out more about occipital nerve stimulation.
Peripheral nerve stimulation
This can used to treat pain in a well defined area of the body such as the groin or part of the face. Electrodes are placed under the skin of the affected area.
Find out more about peripheral nerve stimulation.
Intrathecal drug delivery
This treatment is used for spasticity and severe pain. An implanted pump is used to deliver very small quantities of drugs directly into the space around the spinal cord. The drugs can be more effective than when taken by mouth, and much smaller quantities are needed, so that side effects may be less.
Find out more about intrathecal drug delivery.
Copyright OFN Tuesday, 10 February, 2015.